pyrpl.hardware_modules package¶
Subpackages¶
Submodules¶
pyrpl.hardware_modules.ams module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.ams.AMS(parent, name=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.HardwareModulemostly deprecated module (redpitaya has removed adc support). only here for dac2 and dac3
-
addr_base= 1077936128¶
-
dac0¶ PWM output 0 [V]
-
dac1¶ PWM output 1 [V]
-
dac2¶ PWM output 2 [V]
-
dac3¶ PWM output 3 [V]
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - sets up the AMS (just setting the attributes is OK)
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.asg module¶
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.asg.Asg0¶ alias of
Asg
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.asg.Asg1¶ alias of
Asg
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.asg.AsgAmplitudeAttribute(address, bits=14, bitmask=None, norm=1.0, signed=True, invert=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.FloatRegisterworkaround to make rms amplitude work
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.asg.WaveformAttribute(options=[], **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.SelectProperty-
default= 'sin'¶
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.DspModule(rp, name)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.HardwareModule,pyrpl.modules.SignalModule-
input¶ selects the input signal of the module
-
inputs¶
-
out1_saturated¶ True if out1 is saturated
-
out2_saturated¶ True if out2 is saturated
-
output_direct¶ selects to which analog output the module signal is sent directly
-
output_directs¶
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets the module up for acquisition with the current setup attribute values.
-
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.InputSelectProperty(options=<function all_inputs_keys>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.SelectPropertya select register that stores logical signals if possible, otherwise the underlying dsp signals
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.InputSelectRegister(address, options=<function all_inputs>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.InputSelectProperty,pyrpl.attributes.SelectRegister
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.all_inputs(instance)[source]¶ collects all available logical inputs, composed of all dsp inputs and all submodule inputs, such as lockbox signals etc.
pyrpl.hardware_modules.filter module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.filter.FilterModule(rp, name)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.DspModule-
inputfilter¶ Input filter bandwidths [Hz]. 0 = off, positive bandwidth <=> lowpass, negative bandwidth <=> highpass.
-
inputfilter_options¶
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets the module up for acquisition with the current setup attribute values.
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.hk module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.hk.HK(parent, name=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.HardwareModule-
addr_base= 1073741824¶
-
digital_loop¶ enables digital loop
-
expansion_N0¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N1¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N2¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N3¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N4¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N5¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N6¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_N7¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P0¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P1¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P2¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P3¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P4¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P5¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P6¶ positive digital io
-
expansion_P7¶ positive digital io
-
i= 7¶
-
id¶ device ID
-
led¶ LED control with bits 1 – 8
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets the HouseKeeping module of the redpitaya up. (just setting the attributes is OK)
-
led LED control with bits 1:8
-
expansion_P0 positive digital io
-
expansion_P1 positive digital io
-
expansion_P2 positive digital io
-
expansion_P3 positive digital io
-
expansion_P4 positive digital io
-
expansion_P5 positive digital io
-
expansion_P6 positive digital io
-
expansion_P7 positive digital io
-
expansion_N0 positive digital io
-
expansion_N1 positive digital io
-
expansion_N2 positive digital io
-
expansion_N3 positive digital io
-
expansion_N4 positive digital io
-
expansion_N5 positive digital io
-
expansion_N6 positive digital io
-
expansion_N7 positive digital io
-
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.iq module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.iq.Iq(rp, name)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.filter.FilterModule-
acbandwidth¶ positive corner frequency of input high pass filter
-
acbandwidths= [0, 4, 9, 18, 37, 75, 151, 303, 607, 1214, 2428, 4857, 9714, 19428, 38856, 77712, 155424, 310849, 621698, 1243397, 2486795, 4973591, 9947183, 19894367, 39788735, 79577471, 159154943]¶
-
amplitude¶ amplitude of coherent modulation [volts]
-
bandwidth¶ Quadrature filter bandwidths [Hz].0 = off, negative bandwidth = highpass
-
bandwidths¶
-
frequency¶ frequency of iq demodulation [Hz]
-
gain¶ gain of the iq module (see drawing)
-
n= 26¶
-
na_trace(start=0, stop=100000.0, points=1001, rbw=100, avg=1.0, amplitude=0.1, input='adc1', output_direct='off', acbandwidth=0, sleeptimes=0.5, logscale=False, stabilize=None, maxamplitude=1.0)[source]¶
-
on¶ If set to False, turns off the module, e.g. to re-synchronize the phases
-
output_signal¶ Signal to send back to DSP multiplexer
-
output_signals= ['quadrature', 'output_direct', 'pfd', 'off', 'quadrature_hf']¶
-
pfd_integral¶ value of the pfd integral [volts]
-
phase¶ Phase shift between modulation and demodulation [degrees]
-
quadrature_factor¶ amplification factor of demodulated signal [a.u.]
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets up an iq demodulator, refer to the drawing in the GUI for an explanation of the IQ layout. (just setting the attributes is OK).
-
input¶ selects the input signal of the module
-
acbandwidth positive corner frequency of input high pass filter
-
frequency frequency of iq demodulation [Hz]
-
bandwidth Quadrature filter bandwidths [Hz].0 = off, negative bandwidth = highpass
-
quadrature_factor amplification factor of demodulated signal [a.u.]
-
output_signal Signal to send back to DSP multiplexer
-
gain gain of the iq module (see drawing)
-
amplitude amplitude of coherent modulation [volts]
-
phase Phase shift between modulation and demodulation [degrees]
-
output_direct¶ selects to which analog output the module signal is sent directly
-
-
transfer_function(frequencies, extradelay=0)[source]¶ Returns a complex np.array containing the transfer function of the current IQ module setting for the given frequency array. The given transfer function is only relevant if the module is used as a bandpass filter, i.e. with the setting (gain != 0). If extradelay = 0, only the default delay is taken into account, i.e. the propagation delay from input to output_signal.
Parameters: - frequencies (np.array or float) – Frequencies to compute the transfer function for
- extradelay (float) – External delay to add to the transfer function (in s). If zero, only the delay for internal propagation from input to output_signal is used. If the module is fed to analog inputs and outputs, an extra delay of the order of 200 ns must be passed as an argument for the correct delay modelisation.
Returns: tf – The complex open loop transfer function of the module.
Return type: np.array(.., dtype=np.complex)
-
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.iq.IqAcbandwidth(default=None, doc='', ignore_errors=False, call_setup=False)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.FilterPropertydescriptor for the acbandwidth of the Iq module
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.iq.IqGain(min=<MagicMock name='mock.inf.__neg__()' id='140551782582288'>, max=<MagicMock name='mock.inf' id='140551782527568'>, increment=0, log_increment=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.FloatPropertydescriptor for the gain of the Iq module
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pid module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pid.IValAttribute(min=<MagicMock name='mock.inf.__neg__()' id='140551782582288'>, max=<MagicMock name='mock.inf' id='140551782527568'>, increment=0, log_increment=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.FloatPropertyAttribute for integrator value
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pid.Pid(rp, name)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.filter.FilterModule-
derivative¶
-
i¶ pid integral unity-gain frequency [Hz]
-
integral¶
-
ival¶ Current value of the integrator memory (i.e. pid output voltage offset)
-
max_voltage¶ maximum output signal [volts]
-
min_voltage¶ minimum output signal [volts]
-
p¶ pid proportional gain [1]
-
proportional¶
-
reg_integral¶
-
setpoint¶ pid setpoint [volts]
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - sets up the pid (just setting the attributes is OK).
-
input¶ selects the input signal of the module
-
output_direct¶ selects to which analog output the module signal is sent directly
-
setpoint pid setpoint [volts]
-
p pid proportional gain [1]
-
i pid integral unity-gain frequency [Hz]
-
inputfilter¶ Input filter bandwidths [Hz]. 0 = off, positive bandwidth <=> lowpass, negative bandwidth <=> highpass.
-
max_voltage maximum output signal [volts]
-
min_voltage minimum output signal [volts]
-
-
transfer_function(frequencies, extradelay=0)[source]¶ Returns a complex np.array containing the transfer function of the current PID module setting for the given frequency array. The settings for p, i, d and inputfilter, as well as delay are aken into account for the modelisation. There is a slight dependency of delay on the setting of inputfilter, i.e. about 2 extracycles per filter that is not set to 0, which is however taken into account.
Parameters: - frequencies (np.array or float) – Frequencies to compute the transfer function for
- extradelay (float) – External delay to add to the transfer function (in s). If zero, only the delay for internal propagation from input to output_signal is used. If the module is fed to analog inputs and outputs, an extra delay of the order of 200 ns must be passed as an argument for the correct delay modelisation.
Returns: tf – The complex open loop transfer function of the module.
Return type: np.array(.., dtype=np.complex)
-
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pid.SignalLauncherPid(module)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.SignalLauncher-
update_ival= <MagicMock name='mock.QtCore.Signal()' id='140551782370384'>¶
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pwm module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.pwm.Pwm(rp, name=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.dsp.DspModuleAuxiliary outputs. PWM0-3 correspond to pins 17-20 on E2 connector.
See http://wiki.redpitaya.com/index.php?title=Extension_connectors to find out where to connect your output device to the board. Outputs are 0-1.8V, but we will map this to -1 to 1 V internally to guarantee compatibility with other modules. So setting a pwm voltage to ‘-1V’ means you’ll measure 0V, setting it to ‘+1V’ you’ll find 1.8V.
Usage: pwm0 = AuxOutput(output=’pwm0’) pwm0.input = ‘pid0’ Pid(client, module=’pid0’).ival = 0 # -> outputs 0.9V on PWM0
Make sure you have an analog low-pass with cutoff of at most 1 kHz behind the output pin, and possibly an output buffer for proper performance. Only recommended for temperature control or other slow actuators. Big noise peaks are expected around 480 kHz.
Currently, only pwm1 and pwm2 are available.
-
output_direct= None¶
-
output_directs= None¶
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets the module up for acquisition with the current setup attribute values.
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.sampler module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.sampler.Sampler(parent, name=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.HardwareModulethis module provides a sample of each signal.
This is a momentary workaround, will be improved later on with an upgraded FPGA version
-
addr_base= 1076887552¶
-
asg0¶ current value of asg0
-
asg1¶ current value of asg1
-
iir¶ current value of iir
-
in1¶ current value of in1
-
in2¶ current value of in2
-
iq0¶ current value of iq0
-
iq1¶ current value of iq1
-
iq2¶ current value of iq2
-
iq2_2¶ current value of iq2_2
-
mean_stddev(signal='in1', t=0.01)[source]¶ computes the mean and standard deviation of the chosen signal
Parameters: - signal (input signal) –
- t (duration over which to average) –
- obsolete –
- n (equivalent number of FPGA clock cycles to average over) –
Returns: mean, stddev
Return type: mean and standard deviation of all samples
-
off¶ current value of off
-
out1¶ current value of out1
-
out2¶ current value of out2
-
pid0¶ current value of pid0
-
pid1¶ current value of pid1
-
pid2¶ current value of pid2
-
setup(**kwds)¶ - Sets the module up for acquisition with the current setup attribute values.
-
stats(signal='in1', t=0.01)[source]¶ computes the mean, standard deviation, min and max of the chosen signal over duration t
Parameters: - signal (input signal) –
- t (duration over which to average) –
- obsolete –
- n (equivalent number of FPGA clock cycles to average over) –
Returns: mean, stddev, max, min
Return type: mean and standard deviation of all samples
-
trig¶ current value of trig
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope.ContinuousRollingFuture(module)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.async_utils.PyrplFutureThis Future object is the one controlling the acquisition in rolling_mode. It will never be fullfilled (done), since rolling_mode is always continuous, but the timer/slot mechanism to control the rolling_mode acquisition is encapsulated in this object.
-
DELAY_ROLLING_MODE_MS= 20¶
-
current_avg= 1¶
-
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope.DecimationRegister(address, bitmask=None, options={}, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.attributes.SelectRegisterCareful: changing decimation changes duration and sampling_time as well
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope.DurationProperty(options=[], **kwargs)[source]¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope.SamplingTimeProperty(options=[], **kwargs)[source]¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.scope.Scope(parent, name=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.modules.HardwareModule,pyrpl.acquisition_module.AcquisitionModule-
addr_base= 1074790400¶
-
average¶ Enables averaging during decimation if set to True
-
ch1_active¶ should ch1 be displayed in the gui?
-
ch1_firstpoint¶ 1 sample of ch1 data [volts]
-
ch2_active¶ should ch2 be displayed in the gui?
-
ch2_firstpoint¶ 1 sample of ch2 data [volts]
-
current_timestamp¶ An absolute counter for the time [cycles]
-
data_length= 16384¶
-
data_x¶
-
dec= 65536¶
-
decimation¶ decimation factor
-
decimations= [1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536]¶
-
duration¶
-
durations= [0.000131072, 0.000262144, 0.000524288, 0.001048576, 0.002097152, 0.004194304, 0.008388608, 0.016777216, 0.033554432, 0.067108864, 0.134217728, 0.268435456, 0.536870912, 1.073741824, 2.147483648, 4.294967296, 8.589934592]¶
-
hysteresis¶ hysteresis for trigger [volts]
-
hysteresis_ch1¶
-
hysteresis_ch2¶
-
input1¶ selects the input signal of the module
-
input2¶ selects the input signal of the module
-
inputs¶
-
name= 'scope'¶
-
pretrig_ok¶ True if enough data have been acquired to fill the pretrig buffer
-
rolling_mode¶ In rolling mode, the curve is continuously acquired and translated from the right to the left of the screen while new data arrive.
-
sampling_time¶
-
sampling_times= [8e-09, 1.6e-08, 3.2e-08, 6.4e-08, 1.28e-07, 2.56e-07, 5.12e-07, 1.024e-06, 2.048e-06, 4.096e-06, 8.192e-06, 1.6384e-05, 3.2768e-05, 6.5536e-05, 0.000131072, 0.000262144, 0.000524288]¶
-
save_curve()[source]¶ Saves the curve(s) that is (are) currently displayed in the gui in the db_system. Also, returns the list [curve_ch1, curve_ch2]...
-
setup(**kwds)¶ -
trace_average¶ number of curves to average in single mode. In continuous mode, a moving window average is performed.
-
curve_name¶ name of the curve to save.
-
input1 selects the input signal of the module
-
input2 selects the input signal of the module
-
duration
-
average Enables averaging during decimation if set to True
-
trigger_source¶ Trigger source for the scope. Use ‘immediately’ if no synchronisation is required. Trigger_source will be ignored in rolling_mode.
Options: [‘off’, ‘immediately’, ‘ch1_positive_edge’, ‘ch1_negative_edge’, ‘ch2_positive_edge’, ‘ch2_negative_edge’, ‘ext_positive_edge’, ‘ext_negative_edge’, ‘asg0’, ‘asg1’, ‘dsp’]
trigger_delay: delay between trigger and acquisition start.- negative values down to -duration are allowed for pretrigger. In trigger_source=’immediately’, trigger_delay is ignored.
- threshold: trigger threshold [volts]
hysteresis: hysteresis for trigger [volts]
ch1_active: should ch1 be displayed in the gui?
ch2_active: should ch2 be displayed in the gui?
xy_mode: in xy-mode, data are plotted vs the other channel (instead of time)
rolling_mode: In rolling mode, the curve is continuously acquired and translated from the right to the left of the screen while new data arrive.
running_state: Indicates whether the instrument is running acquisitions or not. See
RunningStatePropertyfor available options.
-
-
st= 0.000524288¶
-
threshold¶ trigger threshold [volts]
-
threshold_ch1¶
-
threshold_ch2¶
-
times¶
-
trigger_debounce¶ Trigger debounce time [s]
-
trigger_delay¶ delay between trigger and acquisition start. negative values down to -duration are allowed for pretrigger. In trigger_source=’immediately’, trigger_delay is ignored.
-
trigger_source Trigger source for the scope. Use ‘immediately’ if no synchronisation is required. Trigger_source will be ignored in rolling_mode. Options: [‘off’, ‘immediately’, ‘ch1_positive_edge’, ‘ch1_negative_edge’, ‘ch2_positive_edge’, ‘ch2_negative_edge’, ‘ext_positive_edge’, ‘ext_negative_edge’, ‘asg0’, ‘asg1’, ‘dsp’]
-
trigger_sources= ['off', 'immediately', 'ch1_positive_edge', 'ch1_negative_edge', 'ch2_positive_edge', 'ch2_negative_edge', 'ext_positive_edge', 'ext_negative_edge', 'asg0', 'asg1', 'dsp']¶
-
trigger_timestamp¶ An absolute counter for the trigger time [cycles]
-
voltage_in1¶ in1 current value [volts]
-
voltage_in2¶ in2 current value [volts]
-
voltage_out1¶ out1 current value [volts]
-
voltage_out2¶ out2 current value [volts]
-
xy_mode¶ in xy-mode, data are plotted vs the other channel (instead of time)
-
pyrpl.hardware_modules.trig module¶
-
class
pyrpl.hardware_modules.trig.Trig(rp, name)[source]¶ Bases:
pyrpl.hardware_modules.filter.FilterModuleThe trigger module implements a full-rate trigger on a DSP signal.
The trigger can be used to assert whether its input signal remains within pre-specified bounds or to record the phase of asg0 at the moment when the trigger was triggered. This makes it comparable in performance to an IQ module.
We plan to enable usage of the trigger module as additional trigger input for the scope, thereby enabling the recording of arbitrary data while triggering on a signal that is not necessarily the trigger source.
-
armed¶ Set to True to arm trigger
-
auto_rearm¶ Automatically re-arm trigger?
-
current_timestamp¶ An absolute counter for the time [cycles]
-
hysteresis¶ hysteresis for ch1 trigger [volts]
-
output_signal¶ Signal to use as module output
-
output_signal_to_phase(v)[source]¶ Converts the output signal value from volts to degrees.
This is useful when
Trig.output_signalis set to a phase and the phase is to be retrieved from a sampled output value.The conversion is based on the following correspondence:
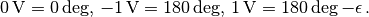
Parameters: v (float) – The output signal value in Volts. Returns: The phase in degrees corresponding to the argument value. Return type: float
-
output_signals= ['TTL', 'asg0_phase']¶
-
phase_abs¶ Output the absolute value of the phase
-
phase_offset¶ offset to add to the output phase (before taking absolute value)
-
setup(**kwds)¶ sets up the module (just setting the attributes is OK). .. attribute:: input
selects the input signal of the module-
output_direct¶ selects to which analog output the module signal is sent directly
-
output_signal Signal to use as module output
-
trigger_source¶ Trigger source
-
threshold¶ trigger threshold [volts]
-
hysteresis hysteresis for ch1 trigger [volts]
-
phase_offset offset to add to the output phase (before taking absolute value)
-
auto_rearm Automatically re-arm trigger?
-
phase_abs Output the absolute value of the phase
-
-
threshold trigger threshold [volts]
-
trigger_source Trigger source
-
trigger_sources= ['both_edge', 'neg_edge', 'off', 'pos_edge']¶
-
trigger_timestamp¶ An absolute counter for the trigger time [cycles]
-
Module contents¶
All modules are extensively discussed in the Tutorial. Please refer to there for more information.
